图文摘要
导语
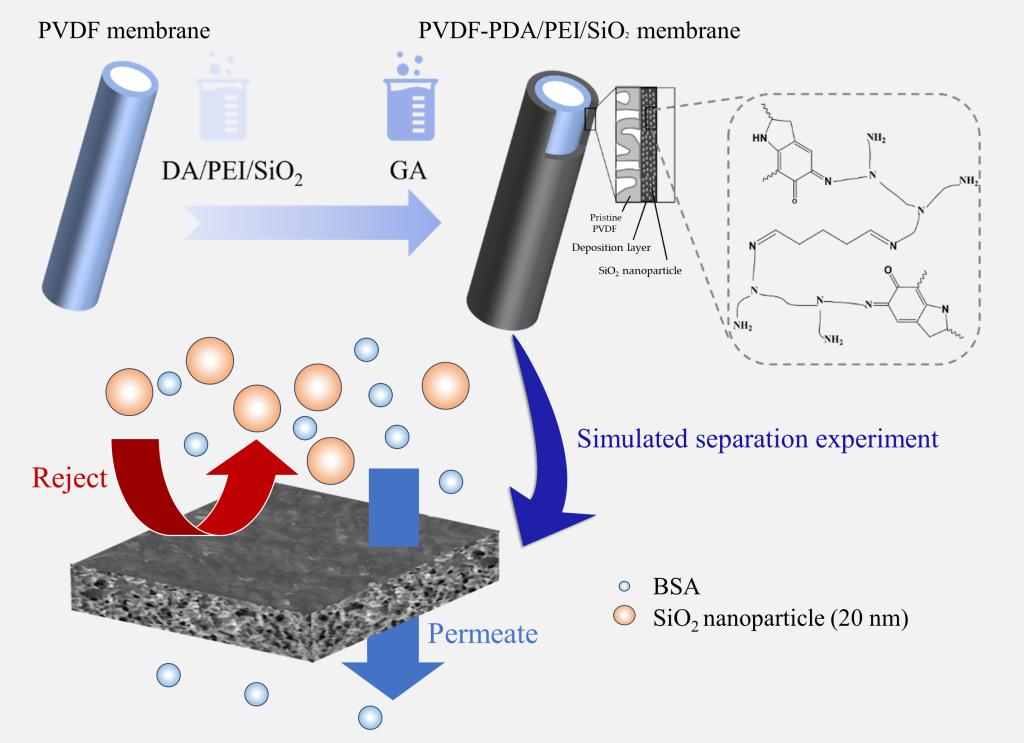
聚偏二氟乙烯(PVDF)膜凭借其卓越的化学稳定性和优异的机械强度,在分离纯化领域有着广泛的应用。然而,PVDF膜在纳米尺度孔径调控方面的挑战以及其固有的疏水性特点,成为了限制其进一步发展的关键难题。近年来众多研究致力于改善膜的亲水性,但对于膜孔径调控的探讨仍显不足。本研究基于多巴胺(DA)、聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)和二氧化硅(SiO2)纳米粒子的共沉积技术,并结合戊二醛交联,成功在膜表面构建具有高度交联结构的选择性分离层,通过控制膜孔径大小并引入亲水基团提高膜表面抗蛋白吸附性能,使得溶液中的杂质颗粒因尺寸大于孔径被截留在原料液一侧,而蛋白质分子可以顺利透过膜孔至渗透液中。本研究为超滤膜/微滤膜的性能调节开辟了新的途径,而且所提出的分离层构建方法条件温和、操作简便、环境友好且成本低廉,在重组蛋白疫苗等生物制药领域的病毒灭活环节中,该方法展现出了广阔的应用前景。
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes have been widely used in the field of separation and purification due to their excellent chemical stability and mechanical strength. However, the challenges in regulating the nanoscale pore size of PVDF membranes and their inherent hydrophobicity have become key challenges limiting their further development. In recent years, numerous studies have been devoted to improving the hydrophilicity of membranes, but there is still insufficient exploration of membrane pore size regulation. This study is based on the co-deposition technology of dopamine (DA), polyethyleneimine (PEI), and silica (SiO2) nanoparticles, combined with glutaraldehyde crosslinking, to successfully construct a selective separation layer with a highly cross-linked structure on the membrane surface. By controlling the pore size of the membrane and introducing hydrophilic groups, the anti-protein adsorption performance of the membrane surface is improved, so that impurity particles in the solution are intercepted on the side of the raw material due to their larger size than the pore size, and protein molecules can pass through the membrane pores to the permeate without obstruction. This study opens up a new way for the performance regulation of ultrafiltration/microfiltration membranes, and the proposed separation layer construction method has the potential to achieve large-scale production due to mild conditions, simple operation, environmental friendliness, and low cost. This method has shown broad application prospects in the virus inactivation process of biopharmaceutical fields such as protein drugs.
总结与展望
本研究基于多巴胺辅助共沉积技术并结合戊二醛交联构建了一种新型复合分离膜的制备策略,可以实现对膜表面选择性分离层形貌结构和性质的调控,得到了对特定尺寸颗粒具有良好分离性能的复合膜。通过加入纳米粒子有效调节了共沉积过程中的聚集体尺寸并引入大量亲水性基团,发展出一种基于共沉积技术的新型复合膜,对膜的亲水性、抗蛋白吸附性能及渗透性能均有明显提升。本研究提出的改性方法能够同时实现对于膜孔径和亲水性的调控,使得制备的复合膜能够高效去除细小杂质(对20nm粒子截留率可达到99%以上),同时确保蛋白质的顺畅透过(牛血清蛋白透过率可达97%以上),有望用于重组蛋白疫苗、抗体、多肽等蛋白质药物体系中细小病毒的高效去除,在生物制药领域的研发和生产中有着极强的应用潜力。此外,由于多巴胺在各类材料表面的普适粘附性,本研究提出的可控分离层的构建方法,可为不同应用领域复合分离膜的设计及制备提供新思路。
In this study, a novel composite separation membrane preparation strategy was constructed based on the dopamine-assisted co-deposition technique and combined with glutaraldehyde cross-linking, which can realize the regulation of the morphology structure and properties of the selective separation layer on the membrane surface, and obtain the composite membranes with good separation performance for particles of specific sizes. By adding nanoparticles to effectively regulate the aggregate size during the co-deposition process and introducing a large number of hydrophilic groups, a novel composite membrane based on the co-deposition technique was developed, which significantly improved the hydrophilicity, anti-protein adsorption performance and permeation performance of the membrane. The modification method proposed in this study can realize the regulation of membrane pore size and hydrophilicity at the same time, so that the composite membrane can efficiently remove fine impurities (the retention rate of 20 nm particles can reach more than 99%), and at the same time, ensure the smooth transmission of proteins (the transmission rate of bovine serum proteins can reach more than 97%), which is expected to be used in the recombinant protein vaccines, antibodies, peptides and other protein drug systems for efficient removal of small viruses, and can be used in biopharmaceuticals. It is expected to be used in recombinant protein vaccines, antibodies, peptides and other protein drug systems for the efficient removal of small viruses, and has a strong potential for application in the R&D and production of biopharmaceuticals. In addition, due to the universal adhesion of dopamine on the surface of various types of materials, the construction method of controllable separation layer proposed in this study can provide new ideas for the design and preparation of composite separation membranes for different applications.
作者简介
通讯作者

林亚凯 副研究员
清华大学 化学工程系
yk_lin@tsinghua.edu.cn
清华大学副研究员、化工系膜技术与工程研究中心副主任,兼任Results in Engineering期刊编委、北京膜学会秘书长、国际水协中国青年委员会委员、中国膜工业协会医药生物膜技术专业委员会委员、中国海水淡化与水再利用学会青年委员会委员。面向生命大健康、饮用水安全、污水资源化等国家重大战略需求,长期致力于分离膜材料开发、应用及产业化的创新研究工作。至今已获得授权专利60余项,发表论文40余篇。